

And to trigger other TARANIS instruments which may point out associated events.

To identify and characterize the strongest lightning flashes,.To locate the source regions of TLEs over the world,.To identify and characterize the TLEs, that is determining their duration, their brightness at different wavelengths, their size, relative location to their parent lightning….The TARANIS originality is that observations are performed at the nadir above the thunderstorms for comparison of light emissions with corresponding X, gamma, radio emissions, instead at the horizon as previous observations from ground or even from space. Among them, the MicroCameras and Photometers instruments (MCP), object of this paper, is in charge of the remote sensing of the sprites and the lightning in optical wavelengths. To reach these objectives, the TARANIS scientific payload is composed of six scientific instrument. Objectives more precisely focus on the determination of the mechanisms at the origin of TLEs and on their effects on the Earth environment.
#Transient luminous events information series#
TARANIS (Tool for the Analysis of RAdiations from lightNIng and Sprites) is a CNES satellite project belonging to Myriade series and dedicated to the study of impulsive transfers of energy between the Earth’s atmosphere and the space environment. It was launched in 2004 and is still working. The first experiment dedicated to TLE limb observations is ISUAL on board the low orbit satellite FORMOSAT-2.
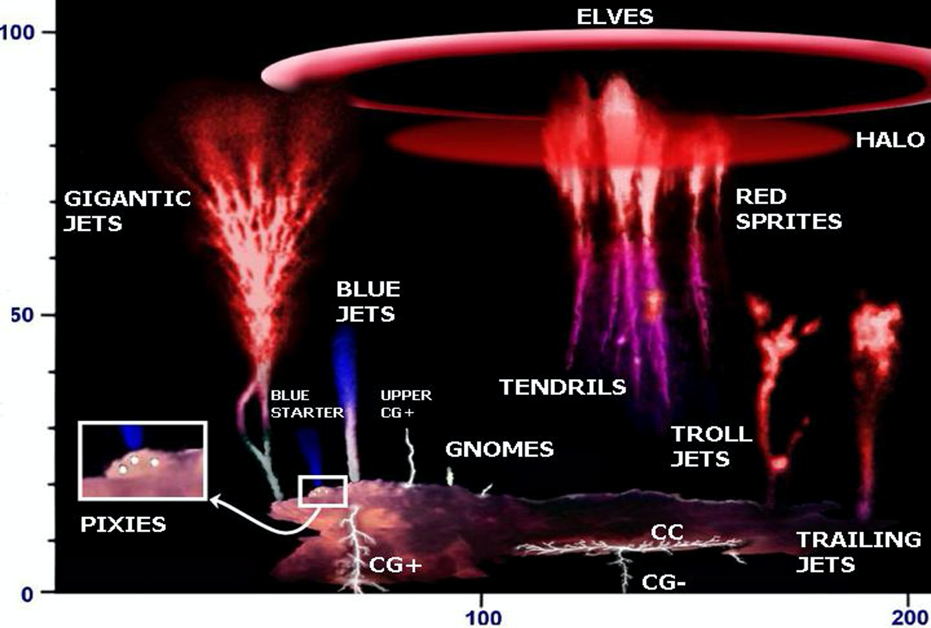
In 2003, the MEIDEX experiment, on board the space Shuttle, measured numerous sprites and elves from oblique and limb directions ]. It was the first experiment observing sprites at nadir. Several years after, the Lightning and Sprite Observations (LSO) experiment has been designed by CEA and CNES and operated by ESA astronauts from 2001 to 2004 on board the International Space Station (ISS). First space images of sprites were extracted from thunderstorm movies taken from the space Shuttle in 1989-1991 ]. The TLE hunt started in USA and it is now organized all around the world and even from space. Transient Luminous Event (TLE) is the name for phenomena occurring over thunderclouds from the top of troposphere to the lower thermosphere (20 to 100 km-altitude). Final performances measured on the flying model are presented. The development of the photometer was submitted to important environmental constraints: mass, available space, vibration, shocks, temperatures… Bertin’s challenge has been to take into account these strong environmental requirements which specific damping mechanical system working at low temperature. These requirements lead to use high sensitivity detectors, special filtering systems in UV channel (180−220nm) and specific optical system to limit the loss of energy and to flatten the optical response over the field of view. The photometer aims at measuring very low light levels with a high signal to noise ratio and with a good uniformity all over an important field of view. Bertin Technology has been assigned the task to design, develop, integrate and validate this optical sensor. One of Taranis satellite instruments is a photometer which goals will be to measure emitted light in 4 different wavelength ranges and to distinguish TLE emission from lightning’s emission. Goal of Taranis satellite which will be launch in 2019 is to collect high resolution data on these TLE. These Transient Luminous Events (TLE) are associated to high energy particle emissions like X rays, gamma rays… They cannot be easily observed from earth because of clouds and atmospheric absorption. In 1990, scientists discovered and started studying the luminous events which occur above storms at altitudes of 20 to 100km.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
